By Sagar P.Dalvi
Trainer in CMS THANE
https://www.facebook.com/sagar.dalvi.1806
Notes for Students
What is Network Topology?
Computer network topology is the way various components of a network (like nodes, links, peripherals, etc) are arranged. Network topologies define the layout, virtual shape or structure of network, not only physically but also logically.
The way in which different systems and nodes are connected and communicate with each other is determined by topology of the network.
Topology can be physical or logical.
Physical Topology is the physical layout of nodes, workstations and cables in the network; while logical topology is the way information flows between different components.
In general, physical topology relates to a core network whereas
logical topology relates to basic network.
Types of Physical Network Topologies
1) Bus Topology
2) Star Topology
3) Ring Topology
4) Mesh Topology
5) Tree Topology
6) Hybrid Topology
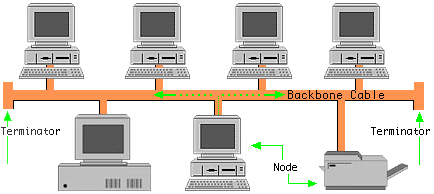
Bus Topology
Bus Topology is the simplest of network topologies. In this type of topology, all the nodes (computers as well as servers) are connected to the single cable (called bus), by
the help of interface connectors.
This central cable is the backbone of the network and is known as Bus (thus the name).
Every workstation communicates with the other device through this Bus.
Advantages (benefits) of Linear Bus Topology
1) It is easy to set-up and extend bus network.2) Cable length required for this topology is the least compared to other networks.
3) Bus topology costs very less.
4) Linear Bus network is mostly used in small networks. Good for LAN.
Disadvantages (Drawbacks) of Linear Bus Topology
1) There is a limit on central cable length and number of nodes that can be connected.
2) Dependency on central cable in this topology has its disadvantages. If the main cable (i.e. bus ) encounters some problem, whole network breaks down.
3) Proper termination is required to dump signals. Use of terminators is must.
4) It is difficult to detect and troubleshoot fault at individual station.
5) Maintenance costs can get higher with time.
6) Efficiency of Bus network reduces, as the number of devices connected to it increases.
7) It is not suitable for networks with heavy traffic.
8) Security is very low because all the computers receive the sent signal from the source.
What is Star topology?
In Star topology, all the components of network are connected to the central device called “hub” which may be a hub, a router or a switch.
Unlike Bus topology (discussed earlier), where nodes were connected to central cable, here all the workstations are connected to central device with a point-to-point connection.
So it can be said that every computer is indirectly connected to every other node by the help of “hub” or “switch”.
All the data on the star topology passes through the central device
before reaching the intended destination. Hub acts as a junction to
connect different nodes present in Star Network, and at the same time it manages and controls whole of the network.
Unshielded Twisted Pair (UTP) Ethernet cable is used to connect
workstations to central node.
Find out what are the advantage and disadvantage of Star topology?
it is very simple think it ?
What is Ring Topology?
In Ring Topology, all the nodes are connected to each-other in such a way that they make a closed loop. Each workstation is connected to two other components on either side, and it communicates with these two adjacent neighbors.
Data travels around the network, in one direction. Sending and
receiving of data takes place by the help of TOKEN.
Token Passing (in brief) : Token contains a piece of information which along with data is sent by the source computer. This token then passes to next node, which checks if the signal is intended to it.
If yes, it receives it and passes the empty to into the network, otherwise passes token along with the data to next node.
This process continues until the signal reaches its intended destination.
Dual-Ring Topology
A network topology in which two concentric rings connect each node on a network instead of one network ring that is used in a ring
topology.
Typically, the secondary ring in a dual-ring topology is
redundant. It is used as a backup in case the primary ring fails.
In these configurations, data moves in opposite directions around the rings.
Each ring is independent of the other until the primary ring fails and the two rings are connected to continue the flow of data traffic.
Dual-ring topology is a network redundant topology where nodes are connected using two concentric rings with four branches. Dual-ring topology is ideal for applications with cabling issues or small networks that are not frequently reconfigured.
Ring topology advantages include:Speed and reliability
Uninterrupted long distance communication
Terminators are not required
Ring topology disadvantages include: Network issues from bad ports or malfunctioning Media Access Unit (MAU) cards
Negative network impact from any added, altered or damaged device
Advantages of Ring Topology
1) This type of network topology is very organized. Each node gets to send the data when it receives an empty token. This helps to reduces chances of collision.
Also in ring topology all the traffic flows in only one direction at very
high speed.
2) Even when the load on the network increases, its performance is better
than that of Bus topology .
3) There is no need for network server to control the connectivity between
workstations.
4) Additional components do not affect the performance of network.
5) Each computer has equal access to resources.
Disadvantages of Ring Topology
1) Each packet of data must pass through all the computers between source and destination. This makes it slower than Star topology .
2) If one workstation or port goes down, the entire network gets affected.
3) Network is highly dependent on the wire which connects different components.
Mesh Topology
In a mesh network topology, each of the network node,
computer and other devices, are interconnected with one
another.
Every node not only sends its own signals but also relays data from other nodes. In fact a true mesh topology is the one where every node is connected to every other node in the network.
This type of topology is very expensive as there are many
redundant connections, thus it is not mostly used in computer networks.
It is commonly used in wireless networks.
Flooding or routing technique is used in mesh topology.
Full Mesh Topology
In this, like a true mesh, each component is connected to everyother component.
Even after considering the redundancy factor and cost of this network, its main advantage is that the network traffic can be redirected to other nodes if one of the nodes goes down.
Full mesh topology is used only for backbone networks.
Partial Mesh Topology:
This is far more practical as compared to full mesh topology.Here, some of the systems are connected in similar fashion as in mesh topology while rests of the systems are only connected to 1 or 2 devices.
It can be said that in partial mesh, the workstations are „indirectly‟ connected to other devices. This one is less costly and also reduces redundancy.
Advantages of Mesh topology
1) Data can be transmitted from different devices simultaneously. This topology can withstand high traffic.2) Even if one of the components fails there is always an alternative present. So data transfer doesn‟t get affected.
3) Expansion and modification in topology can be done without
disrupting other nodes.
Disadvantages of Mesh topology
1) There are high chances of redundancy in many of the network connections.2) Overall cost of this network is way too high as compared to other network topologies.
3) Set-up and maintenance of this topology is very difficult.
Even administration of the network is tough.
What is Tree Topology?
Tree Topology integrates the characteristics of Star and Bus Topology . Earlier we saw how in Physical Star network Topology , computers (nodes) are connected by each other through central hubHybrid Topology ?
Hybrid, as the name suggests, is mixture of two different things. Similarly in this type of topology we integrate two or more different topologies to form a resultant topology which has good points(as well as weaknesses) of all the constituent basic topologies rather than having characteristics of one specific topology.This combination of topologies is done according to the
requirements of the organization.
By Sagar P Dalvi
Trainer in CMS THANE
https://www.facebook.com/sagar.dalvi.1806











This comment has been removed by the author.
ReplyDeleteThank you!!
ReplyDelete